Juan de la Cosa
|
|
|
| Juan de la Cosa was a Spanish sea captain who sailed with
Columbus to the new world on his first three voyages. On the first trip,
the sailed from the port of Palos, in Spain, on August 3, 1492. He was the
owner of the flag ship of the expedition, the Santa Maria. He was an experienced
navigator and pilot, that help Columbus very much on their
voyages. They discovered the new world on October 12, 1492 when they
landed on an island in the Bahamas. From there they explored the
north-eastern coast of Cuba and the northern coast of Española, before
returning to Spain.
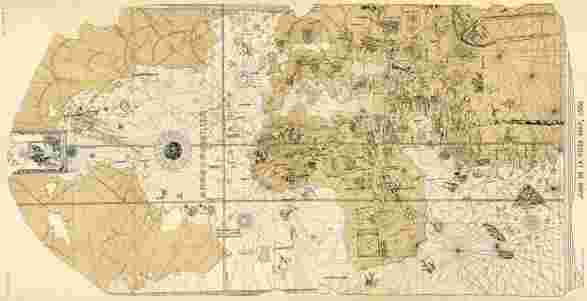
On Columbus' second voyage (1493 - 1496), de la Cosa was the master and cartographer of the Marigalante. On November 3rd, 1493, they sighted the island of Dominica, in the West Indies. The fleet crisscrossed the Caribbean and discovered many islands in the process. There were so many island, the Columbus named the "Las Mil Virgenes" (One Thousand Virgins). He arrived in Española on November 22. The explored the southern side of Cuba, and then the southern side of Española, and on March 10th, 1496, Columbus set sail to Spain. On Columbus' third voyage to the New World (1498 - 1500), de la Cosa was on the ship La Niña. They arrived on the coast of South America on July 31, 1498 making them the first to see the South American continent. From there they sailed to Española, where in 1500, Columbus was arrested and sent back to Spain in chains. On this trip, de la Cosa, was one of the signers to the Perez-Luna agreement, which stated that Cuba was a continent. He signed, under the orders of Columbus, although he was sure that was not the case. Columbus remarked: "Juan de la Cosa thinks he knows more than I do in the art of navigating". Juan de la Cosa's fourth voyage to the New World, was in 1499, when he was the pilot for the expedition of Alonso de Ojeda. They discovered present day Venezuela and sailed along the coast as far as Cabo de Vela. Another distinguished member of that expedition was Americo Vespucci. Juan de la Cosa's fifth voyage to the New World, was with Rodrigo Bastidas. They left Spain on October, 1500, and explored the northern coast of South America, reaching present day Colombia and Panama. In 1503, the King and Queen of Castilla and Aragon, sent de la Cosa to Lisbon, Portugal, to collect information on what were the intensions of the Portuguese with respect to the New World. He was caught and arrested, and released, shortly after. When he got back to Spain, he presented his famous "Mappa Mundi", which was a map of the known world, including the New World. This map is dated 1500. |
|
|
|
| In 1506, Juan de la Cosa was on his sixth trip to the New
World. This time, it was his expedition, and he sailed to Uraba where he
was able to amass a small fortune in gold, that was taken from the
natives, in the area of Darien. He returned to Spain with close to 500,000
marabies.
Queen Isabela, appointed him to a post in the Junta de Burgos. Others appointed to the Junta, were Vicente Yañez Pinzon, Americo Vespucci and Diaz de Solis. In 1508, Juan de la Cosa, embarked on his seventh voyage to the New World. This time he accompanied Alonso de Ojeda, on trip to colonize Tierra Firme, on the coast of present day Colombia. Ojeda and his men where ambushed by the natives in Turbaco where de la Cosa shoot with poison arrows and was killed, in an effort to cover Ojedas's retreat. |